- small trials in surgical patients, where stockings can be applied before immobility, have suggested that they reduce the risk of DVT
- however the large CLOTS 1 trial has conclusively shown that graduated compression stockings do not reduce the risk of DVT after stroke
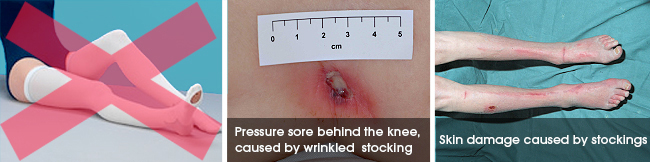
- they are difficult to fit, apply and maintain
- patients find them uncomfortable
- they cause pressure sores and skins problems in 5% of patients
- they waste valuable nursing resources
- NICE and ESO VTE guidelines recommend that GCS should not be used in stroke patients
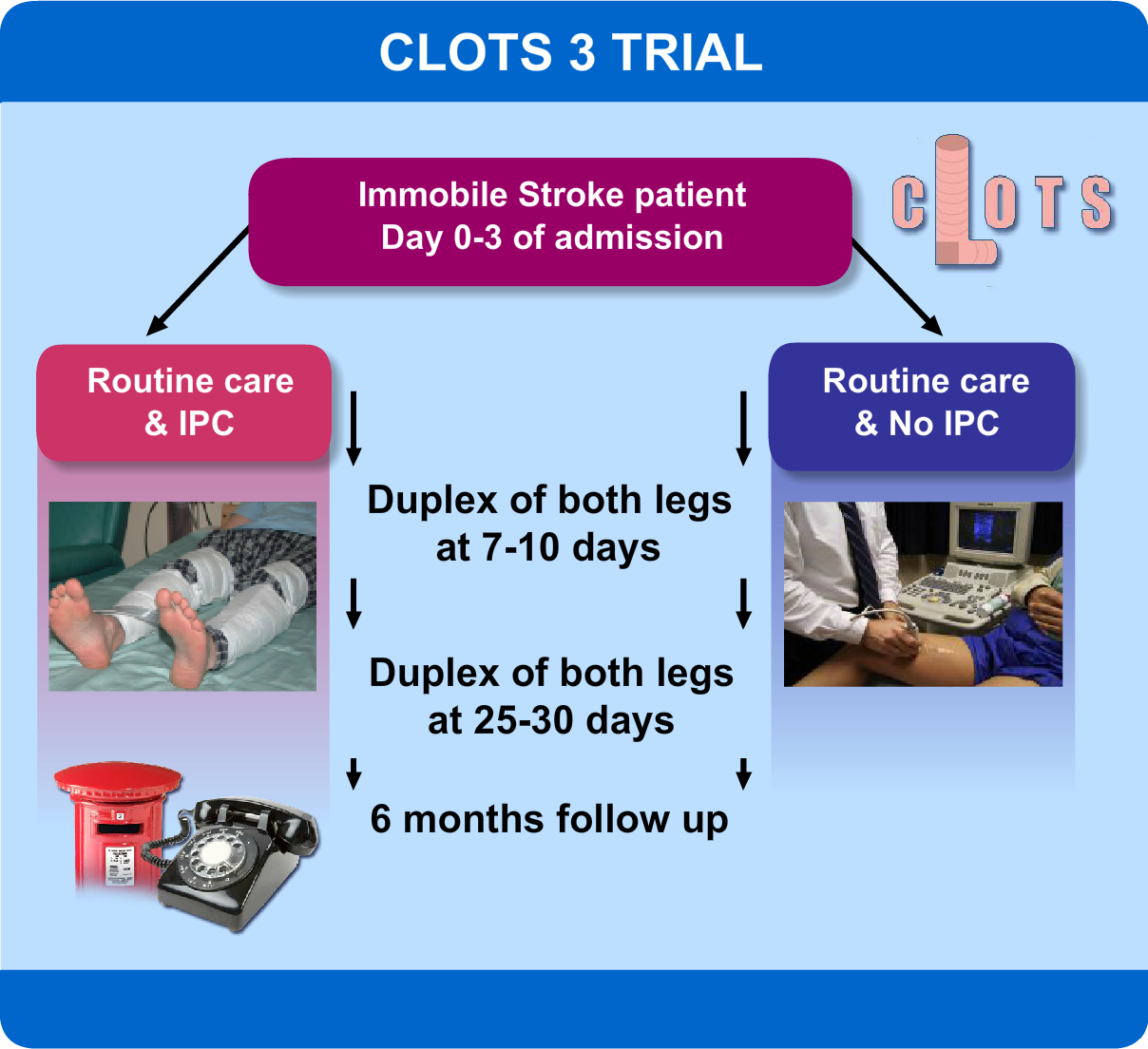
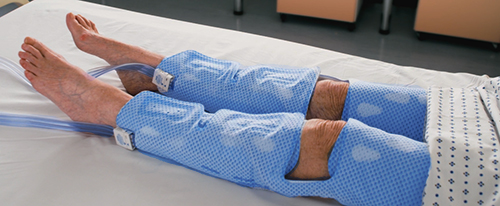
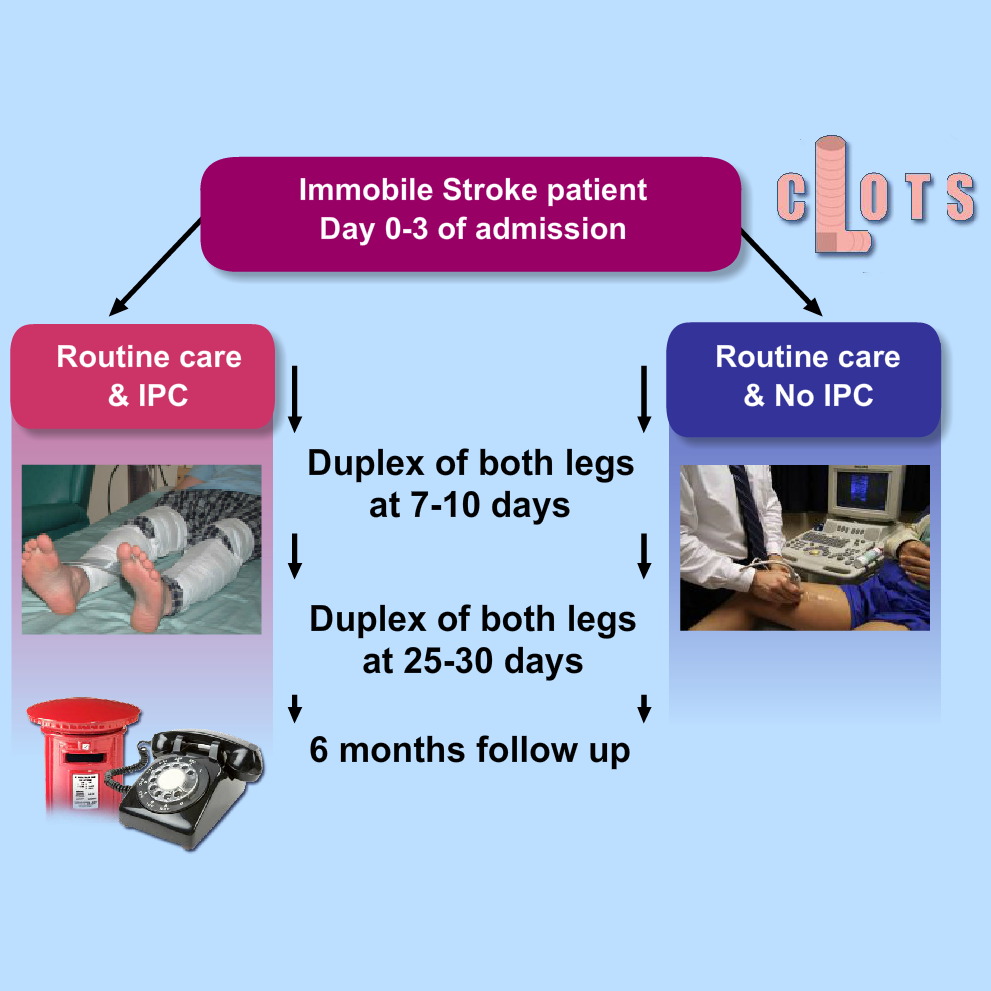
CLOTS Trials Collaboration. Effectiveness of thigh-length graduated compression stockings to reduce the risk of deep vein thrombosis after stroke. Reference: (CLOTS Trial 1): a multicentre, randomized controlled trial. Lancet 2009;373:1958-1965. CLOTS Trial 1 paper. CLOTS Trial 1 content from STARs Advancing Module 11. CLOTS trial design
Before starting a patient on prophylactic heparin or low molecular weight heparin the risk (bleeding) and benefits (avoiding DVT and PE) need to be carefully considered. Identifying patients who will definitely benefit from anticoagulation is not easy.
These do reduce the risk of DVT but:
- They significantly increase the risk of important bleeding
- No significant reduction in deaths
- No improvement in functional outcomes
- They are not recommended for routine use after stroke by Intercollegiate (NICE) OR ESO VTE guidelines for ischaemic stroke
- LMWH may be used in patients at high risk of DVT AND low risk of bleeding
- But unclear how these are defined
Reference:
Lederle FA, Zylla D, MacDonald R, Wilt TJ. Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis in Hospitalized Medical Patients and Those With Stroke: A Background Review for an American College of Physicians Clinical Practice Guideline. Ann Intern Med 2011;155:602-615. Link to paper.
Aspirin is given to most patients with an ischaemic stroke because it has been shown to reduce the risk of recurrence and a poor outcome (death or disability). The first International Stroke trial (IST-1) also showed that the risk of pulmonary embolism was reduced slightly.
The International Stroke Trial, 1997.
ESO VTE guidelines for ischaemic stroke
Angela’s pathway
Angela’s pathway was fairly straight forward – typical for a patient who is suitable for thrombolysis but not thrombectomy.
Outcome
Iain makes a rapid recovery with no complications from the procedure. On the second day he is transferred from the HASU to the stroke unit but within two days he has only a minor speech deficit.
He is discharged home with follow up in the community. He continues on Apixaban to reduce the risk of a further ischaemic stroke.
Key messages
- Patients on oral anticoagulants are not usually eligible for thrombolysis (unless on Warfarin and INR <1.6)
- Thrombectomy is an effective treatment for patients with Large Artery Occlusion (LAO) who cannot receive thrombolysis
- Time is Brain – delays in delivering thrombectomy need to be minimised
- Thrombectomy is a complex procedure, delivered by a team of experts in a specialist facility
- Thrombectomy has some major complications – those caring for patients after the procedure need to be alert to these and know how to provide immediate treatment.