Category: Advancing Modules
Training and support for conversation – partners
In the early stages of rehabilitation, the SLT meets with Steven and his family to provide information for supporting conversation and to begin conversation partner training.
Steven’s youngest son Michael discusses that he struggles to communicate with his Dad. Steven and Michael both end up feeling frustrated at times.
The SLT provides information about aphasia and the communication strategies and resources that can be successful in supporting conversation and connecting with each other.
Through a series of meetings, Steven and his family practise and discuss these strategies and techniques with the SLT.
Watch the video and observe how, by using some basic supported communication techniques, Michael and Steven’s interaction changes.
Supported communication strategies – expression
Supported communication Strategies – understanding
Steven has indicated through facial expression and visual resources that he finds certain strategies helpful to support his understanding of speech and conversation.
Calculating the correct dosage
Angela’s weight is 58 kg. Using the chart below calculate the correct IV bolus and infusion dose for Angela.
| Body Weight (Kg) | Approx. Body Weight (Imperial) | Total rTPA dose (mg) | IV Bolus 10% of total dose (ml) | IV Infusion 90% of total dose (ml/hr) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 6st 4 | 36 | 4 | 32 |
| 42 | 6st 8 | 38 | 4 | 34 |
| 44 | 6st 13 | 40 | 4 | 36 |
| 46 | 7st 3 | 41 | 4 | 37 |
| 48 | 7st 7 | 43 | 4 | 39 |
| 50 | 7st 12 | 45 | 5 | 40 |
| 52 | 8st 2 | 47 | 5 | 42 |
| 54 | 8st 7 | 49 | 5 | 44 |
| 56 | 8st 11 | 50 | 5 | 45 |
| 58 | 9st 1 | 52 | 5 | 47 |
| 60 | 9st 6 | 54 | 5 | 49 |
| 62 | 9st 10 | 56 | 6 | 50 |
| 64 | 10st 1 | 58 | 6 | 52 |
| 66 | 10st 5 | 59 | 6 | 53 |
| 68 | 10st 9 | 61 | 6 | 55 |
| 70 | 11st | 63 | 6 | 57 |
| 72 | 11st 4 | 65 | 6 | 59 |
| 74 | 11st 9 | 67 | 7 | 60 |
| 76 | 11st 13 | 68 | 7 | 61 |
| 78 | 12st 3 | 70 | 7 | 63 |
| 80 | 12st 8 | 72 | 7 | 65 |
| 82 | 12st 12 | 74 | 7 | 67 |
| 84 | 13st 3 | 76 | 8 | 68 |
| 86 | 13st 7 | 77 | 8 | 69 |
| 88 | 13st 12 | 79 | 8 | 71 |
| 90 | 14st 2 | 81 | 8 | 73 |
| 92 | 14st 6 | 83 | 8 | 75 |
| 94 | 14st 11 | 85 | 8 | 77 |
| 96 | 15st 1 | 86 | 9 | 77 |
| 98 | 15st 6 | 88 | 9 | 80 |
| 100 | 15st 10 | 90 | 9 | 81 |
| > 100kg, use 90 mg maximum | ||||
The thrombolysis is started.
The next stage
Giving thrombolysis treatment – Alteplase
Patients admitted with stroke within four and a half hours of definite onset of symptoms who are considered suitable, should be treated with intravenous alteplase 0.9mg/kg/body weight, up to a maximum of 90mg (Grade A evidence).
Diluted with sterile water to 1mg/ml 10% of the total dose is administered as an initial intravenous bolus over 2 minutes, the remaining 90% is administered as an infusion using syringe pump over 1 hour.
The thrombolysis dosage is calculated on the patient’s weight, that is 0.9 mg/kg up to a maximum of 90 mg tPA.
To obtain an accurate weight you could:
- Use a weighing PAT slide
- Roll the trolley onto portable scales
- Transfer the patient using a weighing hoist
- Normal scales if the patient can transfer or stand safely
- Ask the patient if they know a recent weight
- Ask their next of kin if the patient is unable to speak
- Review the patient’s medical records to see if they have been weighed recently
For more detailed information on Alteplase see:
Other possible complications
Indicate which of the 5 signs are likely to indicate that Angela has an extracranial bleed or angio-oedema? True or False:
Should Angela be offered thrombolysis?

Angela is a 65 year old lady who was previously healthy and well. She presented with a right sided facial and upper and lower limb weakness and right homonymous hemianopia. Her blood pressure is 160/90. The CT scan results are below. No contraindications have been identified. Time of onset of symptoms was 7.40am, it is now 9am.
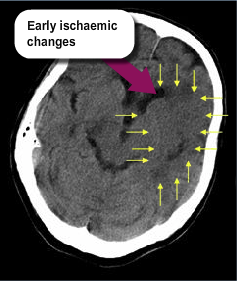
There is some swelling, loss of distinction between grey and white matter so that the basal ganglia and cortex are no longer visible. Confusingly grey matter (i.e. parts of the brain where the cell bodies and nuclei of the neurones are) appears whiter on CT scans than grey matter (i.e. the brain tissue made up of the fibres connecting neurones together).
Ischaemic changes occur as a result of a blockage of the blood flow to an area of the brain, which causes brain cells in the area to die.
What does the CTA show?
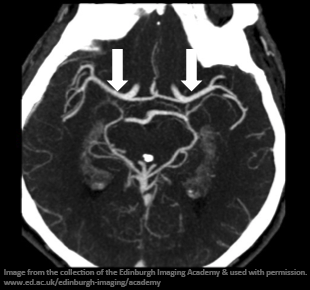
There is no evidence of a large artery occlusion or other abnormality of the extracranial or intracranial vessels.
Select the correct answer below about Angela’s treatment:
Prioritising actions to facilitate early thrombolysis
The CT and CTA have been requested.
Things to do whilst waiting for the CT scan
View text alternative for feedback on each of the priorities.
It is important not to waste time on things which can be done after the thrombolysis has been given.
Resources
Further resources
NES: IPAAKS Informing and Profiling Augmentative and Alternative Communication(ACC) Knowledge and Skills[PDF] This learning resource is available on TURAS Learn. (NHS Education for Scotland).


