Based on Jason’s presenting symptoms, a stroke is the most likely diagnosis. However, other diagnoses need to be considered.
Category: Advancing Modules
At A&E
The doctor in A&E takes a history and establishes that Jason has had a gradual onset of symptoms over the past 2 days. On further questioning the doctor also establishes that Jason smokes, drinks excessive alcohol and regularly takes recreational drugs. (See Topic Loops below)
Examination shows that Jason has:
- mild weakness of his left face, arm and leg
- no problems with speech, vision or neglect
Cardiac examination showed a normal pulse, BP 160/90 and normal heart sounds and peripheral pulses.
Topic Loops:
The following day
Jason spends the following day lying on the sofa watching DVDs and refusing his usual alcoholic drinks. He complains of increasing weakness in his left arm and leg.

Concerned, his partner Suzanne calls NHS 24 who advise them to go straight to the hospital.
Case 4: Jason

Scenario

Jason is a 39 year old man living with his partner. He is a heavy drinker (see Topic Loop below), unemployed, plays snooker and watches TV sport.
He woke on Sunday morning with weakness and numbness in his left arm and leg. He discusses these symptoms with his partner and they decide it is a hangover. Jason got himself dressed and is able to walk around. He has a mild headache which he believes is related to his week-end excesses.
He has no medical history.
Topic Loops:
Key Messages
- Investigate for underlying risk for stroke.
- Iain had narrowing in his carotid arteries. Early identification and management including interventions for carotid artery stenosis lead to better outcomes.
- Prioritising risk factors – Iain had a number of risk factors to consider including smoking, drinking too much alcohol and high blood pressure. Remember that the health professional’s priorities are not always the same as the patient’s.
- Be aware of the different types of services and products available to assist a patient to change their lifestyle.
- Iain was unable to make the change at first and this is common. Setting goals is an important part of making change
What happens to Iain?

Iain continues to enjoy his golf and is participating in a smoking cessation programme. He is beginning to acknowledge that his alcohol intake should be reduced but for now is concentrating on stopping smoking.
Iain sees the practice nurse for monitoring his blood pressure and has been diagnosed as diabetic – his wife is watching his diet carefully!
How can we help Iain to stop smoking?
- Refer Iain to his local smoking cessation team.
- Provide him with CHSS smoking cessation leaflet.
- Refer him to the Selfhelp4stroke free online self management resource.
More information for professionals on self management is available from AM 15: Self Management

CHSS supports the Charter for a smoke-free generation in Scotland by 2034 to protect young people and support positive health choices.
Topic Loop:
What are Iain’s risk priorities?
Iain has never considered the risks associated with smoking and drinking too much alcohol. On a readiness to change scale he scores himself 1-2.
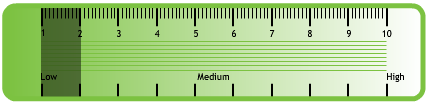
The nurse explains the relationship between the narrowing of arteries and smoking (see Topic Loop below )and also the benefits of keeping within safe alcohol limits. Iain has been shocked by the need for surgery and decides that stopping smoking is his priority. When asked to re-score himself on the readiness to change ruler he now scores 7-8.
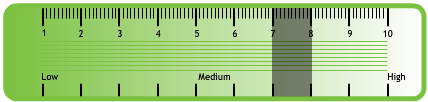
He asks the nurse what help there is available. For further information on behaviour change see Topic Loop below.
Please see the ‘Additional Information’ box below for more information on using the Readiness to Change Ruler.
Topic Loops:
Review meeting
Iain and his wife attend the stroke nurse clinic following his surgery. The stroke nurse wants to consider lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of further events. To gather more information the nurse asks Iain to describe a normal day.
Iain describes his normal day to the nurse. Go through the slides below to see the entries in his diary and compare the results of his wife’s version of his day.
The stroke nurse calculates that Iain consumes approximately 40 units of alcohol per week – see Topic Loop below for further information. When she points this out to Iain he is defensive and he says he is only a social drinker and never gets drunk. His wife then mentions that she thinks he also smokes too much and takes too much salt in his diet.
Topic Loops:
Risks and benefits
What are the risks and benefits?
- In carefully selected patients carotid endarterectomy will substantially reduce the risk of stroke – the reduction in risk is greater, the earlier surgery is performed.
- About 2-3% of patients will have a stroke within a few days of the operation. NHS UK (2018)
- Following surgery some patients will experience a sore throat and neck and their voice may be hoarse.
- Often there is a patch of numbness around the neck wound which can last for some months, but eventually resolves. More permanent nerve damage is fortunately very rare.


